Nowadays, you can find electronics almost everywhere. There are sensors, screens, batteries and integrated circuits wherever you look as a result of the increasing digitization of offices, homes, even cities and, of course, means of transport.
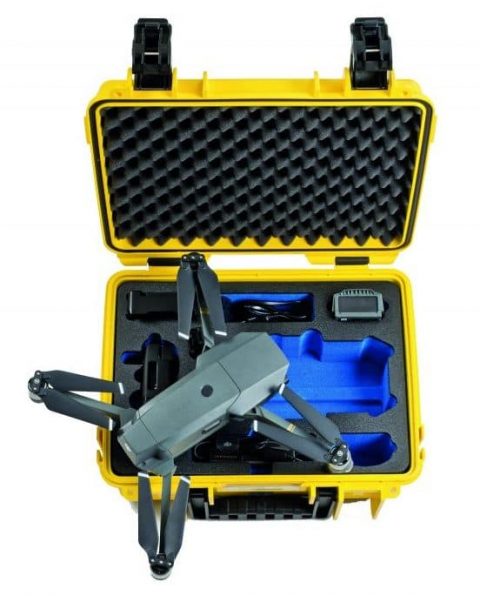
Aside from being a logical and necessary step in aid of the environment, the rise of electric vehicles is an unstoppable snowball. However, electric vehicles incorporate a great many highly sensitive electronic components. It is at this point when the use of foams with dielectric properties (electrical insulators that do not easily conduct current) is necessary to provide proper containment and protection.
However, before contemplating the foams available at ZFoam for these applications, we would like to provide a brief overview of certain aspects of static electricity, offering you a clearer understanding of how each of these mediums behaves.

What is static electricity?
Static electricity is immobile electrical energy. All materials consist of atoms, comprising a positively charged nucleus around which one or more electrons move. If the nucleus gains or loses electrons (for example, when two objects come into contact and then separate) an imbalance occurs. This accumulation of unbalanced charge is what is known as static electricity.
What is an electrostatic discharge?
An electrostatic discharge is a phenomenon where the energy accumulated in a material finds an escape route through a body, which is perceived as a “spark”. One must not forget that static electricity can be a major problem in environments where there are delicate electronic components (e.g., any electric vehicle); hence, it is so important to work with foams that act against this risk.
What can we do to prevent electrostatic discharges?
The use of anti-static materials that reduce or prevent the development or accumulation of static electricity is the key to preventing discharges. Enough moisture is retained by these materials to provide electrical conduction; by contrast, dry environments facilitate its accumulation.
Thus, anti-static materials are great for simple protection and to protect other devices, preventing possible damage to electrical or electronic components resulting from an electrostatic discharge.
What kind of anti-static materials are there?
In general, we would say there are the following materials (with different properties to prevent electrostatic discharges):
- Anti-static: minimising the accumulation of a surface-based static charge and preventing accumulation, but not quickly grounding/dissipating the charge. Resistivity is generally109 and 112 ohms per square metre.
- Dissipative Static: dissipating accumulated a static charge more quickly and preventing discharges arising from human contact. In this case, resistivity is between106 y 109 ohms per square metre.
- Conductive: these materials are very efficient at dissipating static charges. Resistivity is between103 y 106 ohms per square metre.
At ZFoam we have a range of special anti-static foams for this type of application, as well as extensive experience in this field, so you can easily find the most suitable foams for your needs.
Our technical sales team is at your service and would be delighted to help you in this or any other matter. Please write to them at: info@zfoam.com.